Cancer
Cancer is a common condition. In Malaysia, 1 in 10 males and 1 in 9 females will develop some form of cancer during their lifetime. The three most common cancers in Malaysia are Breast, Colorectal and Lung Cancer.
Being aware of signs and symptoms linked to the condition can help in early detection. This is important because the earlier a cancer is detected, the better the chances of successful treatment.
What is Cancer?
Cancer is the general name for a group of diseases, which affect the body’s cells. Although there are many different kinds of cancer, all cancers are caused by abnormal cells growing out of control.
Cancer cells can invade other tissues through the blood and lymph systems. Untreated cancers can cause serious illness and death.
What are cells?
Our bodies are made up of tiny building blocks called cells. Usually, cells grow in a controlled way. Each cell knows exactly what to do, when to do it and when to stop.
During our early years, normal cells divide faster to allow us to grow. After we become an adult, most cells divide only to replace worn-out or dying cells or to repair injuries.

How Does Cancer Begin?
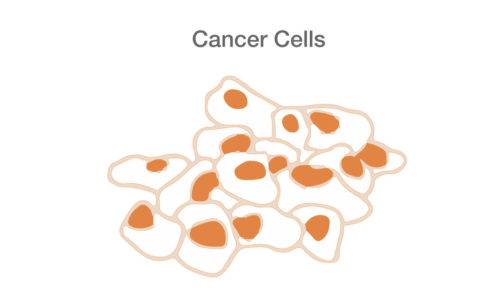
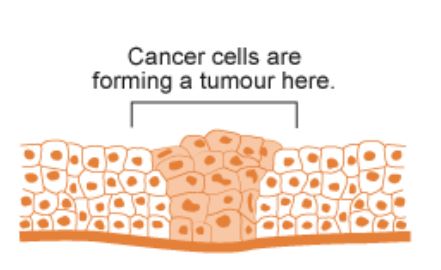
Cancer begins when cells in a part of the body divide without control. Unlike normal cells, cancer cells keep on dividing, forming a lump or tumour. Tumours are either benign (non- cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
Benign tumours can cause problems, but they are not normally as dangerous as cancer. In a malignant tumour, the cancer cells can spread beyond the original area of the body. If the tumour is left untreated, it may spread into surrounding tissue.
How Does Cancer Spread?
Cancer cells can also spread to distant parts of the body. They normally do this by getting into the bloodstream or the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system makes and stores cells that fight infection.
The bloodstream and lymphatic system are, if you like, transport networks in the body. Cancer cells have the ability to move around the body using these networks. If the cells get stuck somewhere, they can begin growing in this new place, forming secondary tumours or metastases
How Do Cancers Differ?
There are many different kinds of cancer – with different signs, symptoms, treatments, and outcomes. Different types of cancer can behave very differently, e.g. lung cancer and skin cancer grow at different rates and respond to different treatments.
This is why people with cancer need treatment that is aimed at their kind of cancer. The most common sites in which cancer develops include the skin, lungs, breasts, prostate, and colon and rectum (large bowel).
What is Cancer Staging?
Cancer stages are used to describe the size and spread of a tumour. Staging helps health professionals to identify the best treatment plan for their patient.
There are four stages:
Stage 0: This usually means the tumour is very small and still in the same place it started.
Stage 1: This usually means the cancer is small in size and located within one organ.
Stage 2: This usually means that the cancer is a bit bigger compared to stage 1. However, it has not spread into other tissues yet. There is a possibility that it has spread into lymph nodes surrounding the organ, which the cancer is located in.
Stage 3: This usually means the cancer is bigger and the tumour may have spread into other tissues and lymph nodes.
Stage 4: This means the cancer has spread into other organs. It is also known as metastatic cancer.
Chances of a cure are much higher if cancer is found and treated early (i.e. Stage 1 and Stage 2).
Therefore, see a doctor urgently if you suspect cancer or notice any warning signs of cancer.
*Source: Information adapted from the Be Cancer Aware Campaign, Northern Ireland; Figures from Malaysian National Cancer Registry Report 2007 – 2011

